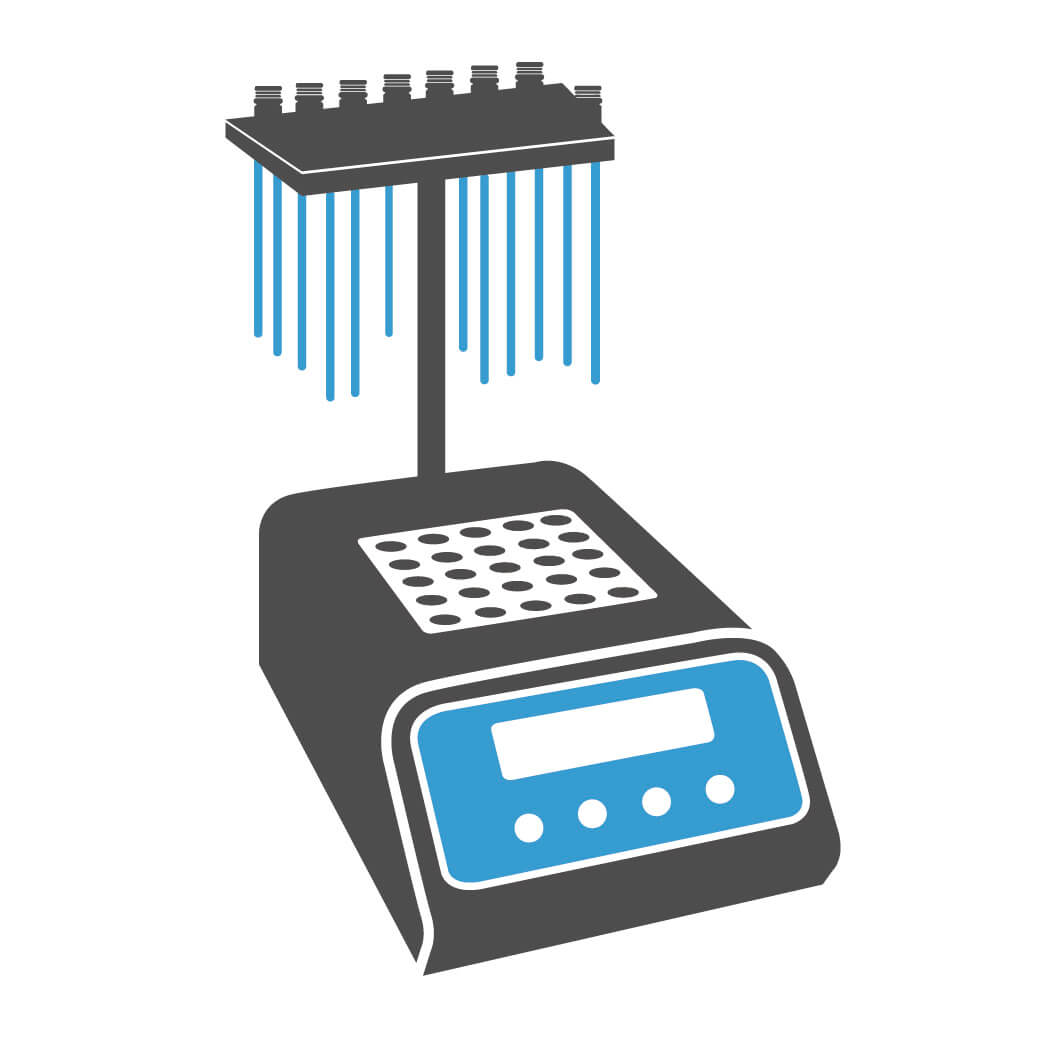
What is centrifugal vacuum concentration?
Factors that affect centrifugal concentrating efficiency
Setting up a centrifugal vacuum concentration system
Comparison of evaporation technologies
Centrifugal concentrator for protein concentration
Centrifugal vacuum concentrator applications
What is centrifugal vacuum concentration?
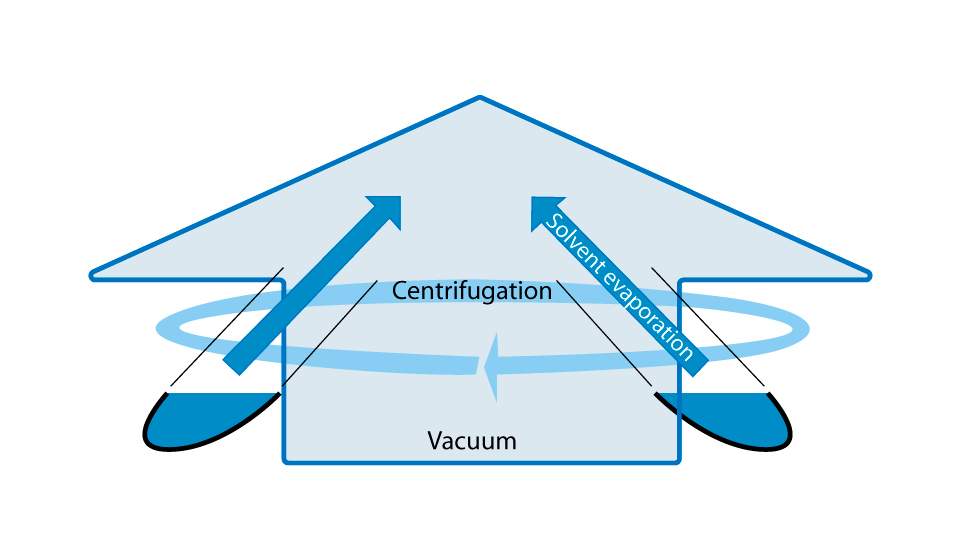
Centrifugal vacuum concentration is a technique used for purification of multiple small-volume samples to dry or wet pellet state simultaneous. The principle of centrifugal concentration is to remove solution continuously and effectively by reducing pressure, which lowers boiling point (bp) of solution, and also applying centrifugal force and heat to reduce the possibility of solvent bumping and shorten evaporation process. As solution gets evaporated, aggressive or even toxic gases may be released. Thus, it is recommended to use with a cold trap, such as circulating or refrigerant condenser, to minimize the risk of solvent emission.
Since most samples to be processed with centrifugal concentrator contain solvent or chemical solution, it’s important to use a chemical resistant vacuum pump to avoid rapid pump damage. Maximum vacuum requirements may differ according depending on boiling point of the substances to be evaporated. Accurate vacuum control is essential to avoid solvent bumping and sample lose.
Factors that affect centrifugal concentrating efficiency
The efficiency and results of centrifugal concentration are influenced by various key factors. Here are explanations for several main factors:
- Vacuum Level:
By increasing the vacuum level (i.e., reducing pressure), the solvent’s boiling point is effectively lowered, helping to accelerate solvent evaporation and reduce the risk of sample loss during the evaporation process. - Temperature:
Moderately increasing the temperature can increase the rate of solvent evaporation. However, for heat-sensitive substances, high temperatures can lead to substance degradation and denaturation. Therefore, temperature adjustments should be made without damaging the sample. - Centrifugal Force:
Centrifugal force not only increases the liquid surface area but also moves the solution towards the bottom, reducing the occurrence of bumping. This can effectively prevent sample loss and cross-contamination. Additionally, it allows the sample to completely settle at the bottom of the centrifuge tube, improving the recovery rate without residue on the tube walls. - Condensation Device:
Effectively condensing and capturing the solvent vapors generated during the concentration process using low temperatures ensures safety, reduces waste, and enhances concentration efficiency.
In addition to the above factors, different sample characteristics, such as viscosity and thermal stability, can also affect concentration efficiency. Therefore, during operation, each parameter should be adjusted according to the specific characteristics of the sample being processed.
Setting up a centrifugal vacuum concentration system
Centrifugal concentration configurations typically include (a) a centrifugal concentrator, (b) vacuum equipment, and (c) condensation equipment. The combined action of these three components can significantly enhance concentration efficiency and reduce solvent loss and potential safety risks.
- (a) Centrifugal Concentrator: This is the main instrument for centrifugal concentration. It accommodates different volumes of concentrated samples by changing the rotor, such as 0.5 mL / 1.5 mL / 2.0 mL Eppendorf tubes or 15 mL / 50 mL centrifuge tubes. When purchasing, please ensure that the selected model has compatible rotors.
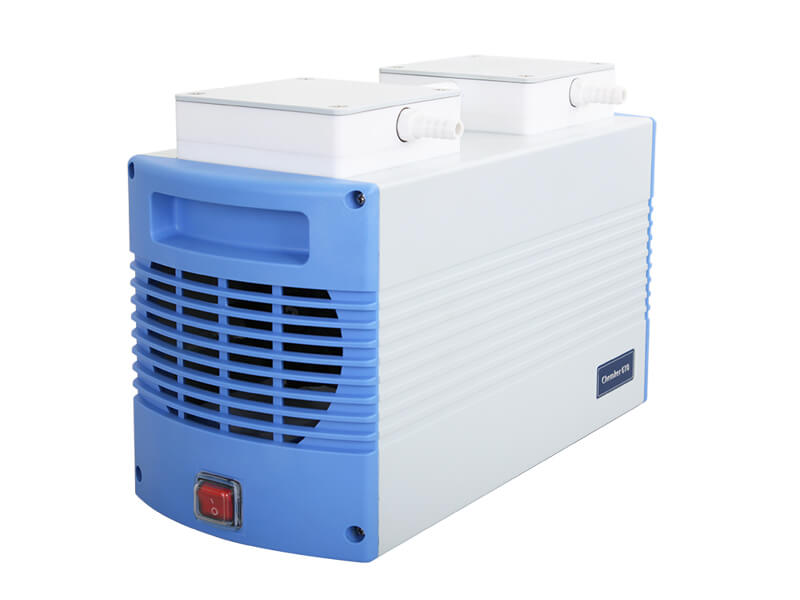
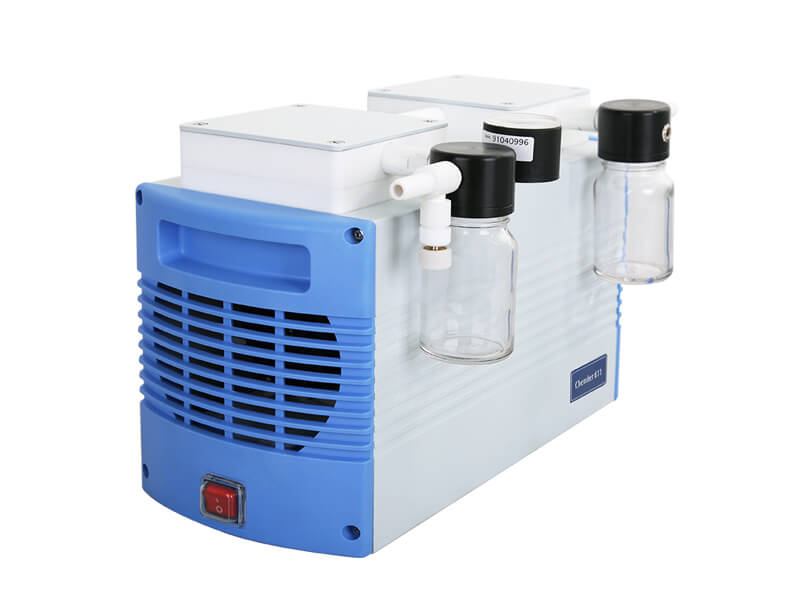
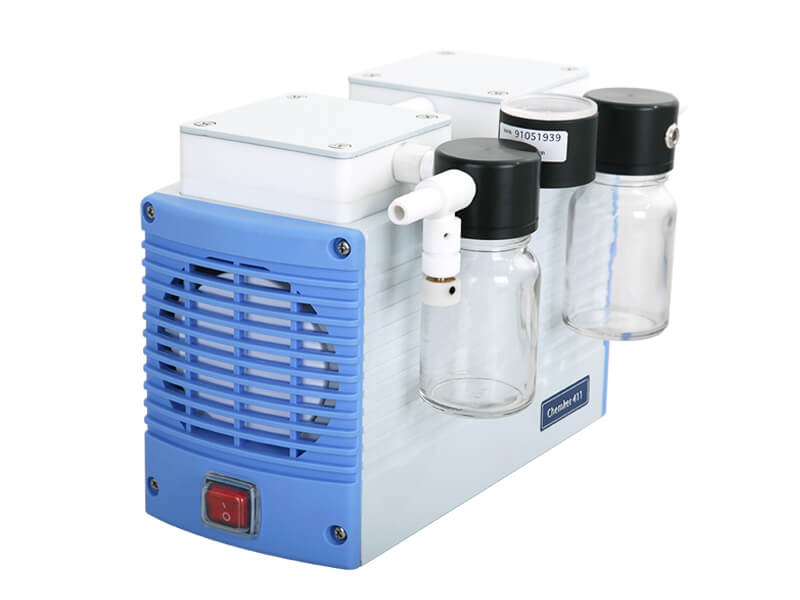
- (b) Vacuum Equipment: During the concentration process, organic solvents are commonly used. It is recommended to use corrosion-resistant vacuum pumps to ensure durability when handling solvents. If the sample is sensitive to pressure fluctuations (pressure-sensitive substances), you can also consider installing a vacuum controller to reduce pressure fluctuations or use an automatic vacuum control system to directly replace the vacuum pump, effectively improving the precision of vacuum control.
- (c) Condensation Equipment: This equipment condenses solvent vapors into liquid, preventing solvent vapors from entering the vacuum pump and causing pump damage, thereby extending the pump’s lifespan. It also prevents solvent vapors from escaping into the environment, posing a hazard to personnel.
Comparison of evaporation technologies
|
Concentration Technologies |
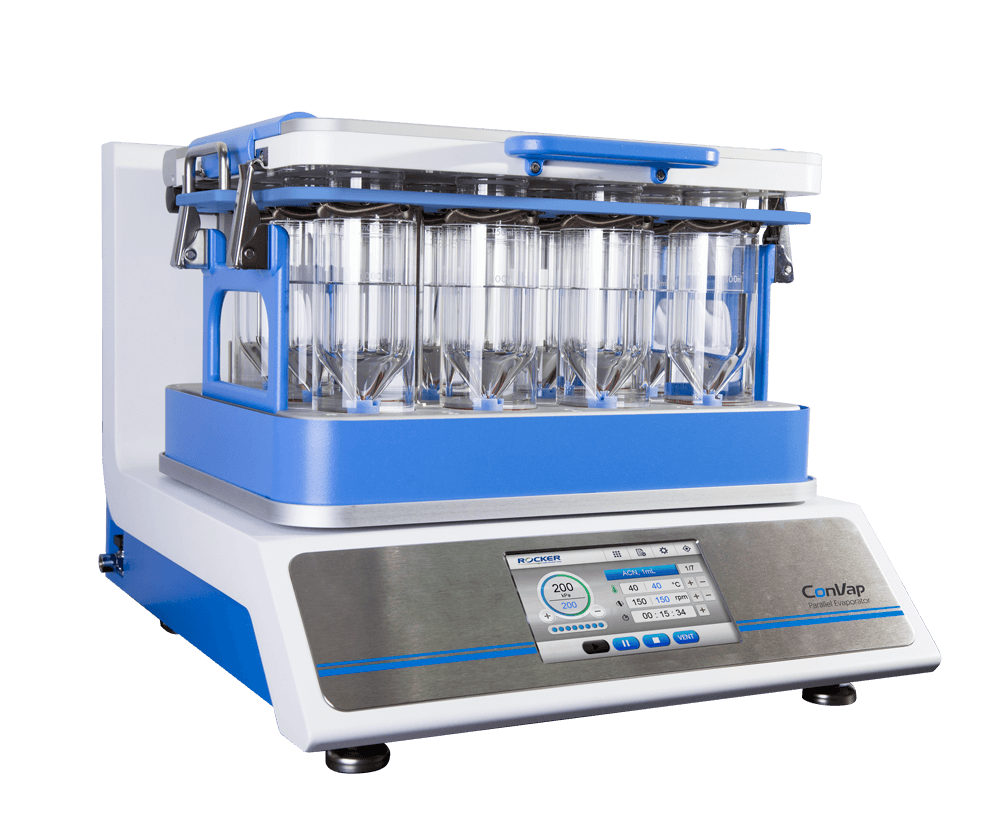
Vacuum Vortex Concentration/ Parallel Evaporator |
Rotary Vacuum Concentration |
Nitrogen Blowdown Concentration |
Centrifugal Vacuum Concentration |
|
|
||||
|
Number of Sample |
Multiple (12 / 48) |
1 (Single) |
Multiple |
Multiple |
|
Parameter Controls |
Vacuum, temperature, RPM, time |
Temperature, RPM |
Temperature, flow speed |
Temperature, RPM, time |
|
Cross-contamination |
Risk-free |
Risk-free |
High risk |
Low risk |
|
Consumable parts |
No |
No |
Nitrogen |
No |
| Visibility |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Tube Loading/ Unloading |
Batch & single |
Single |
Batch & single |
Single |
|
Solvent Vapor Collection |
Yes. In-room. |
Yes. In-hood. |
No. In-hood. |
Yes. In-room. |
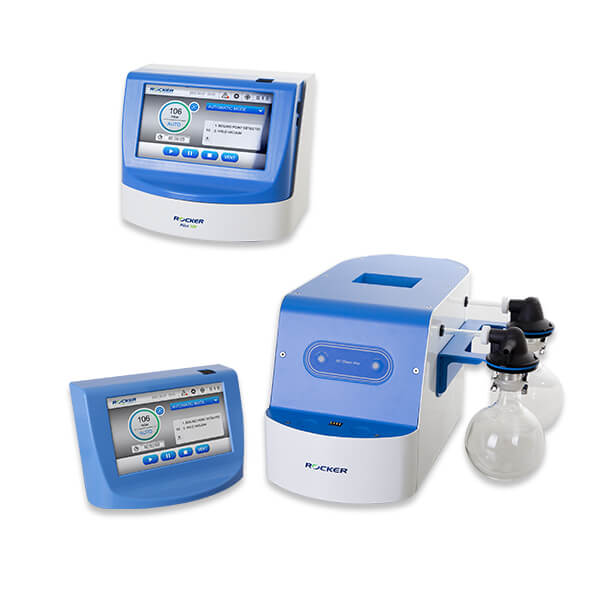
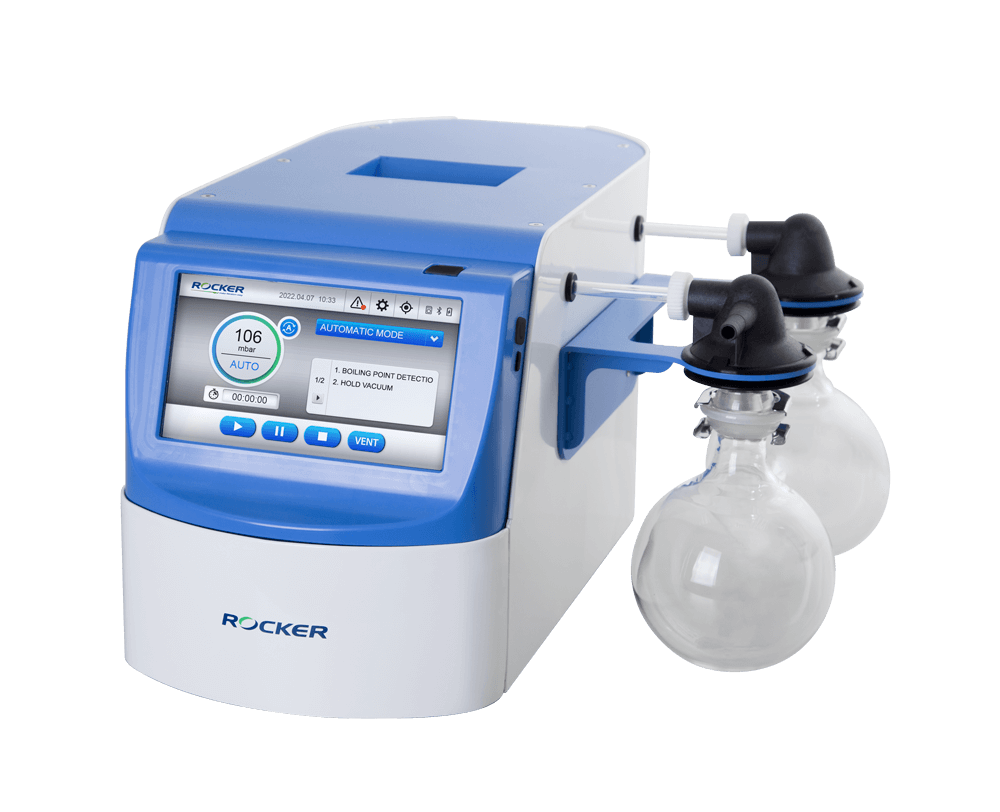
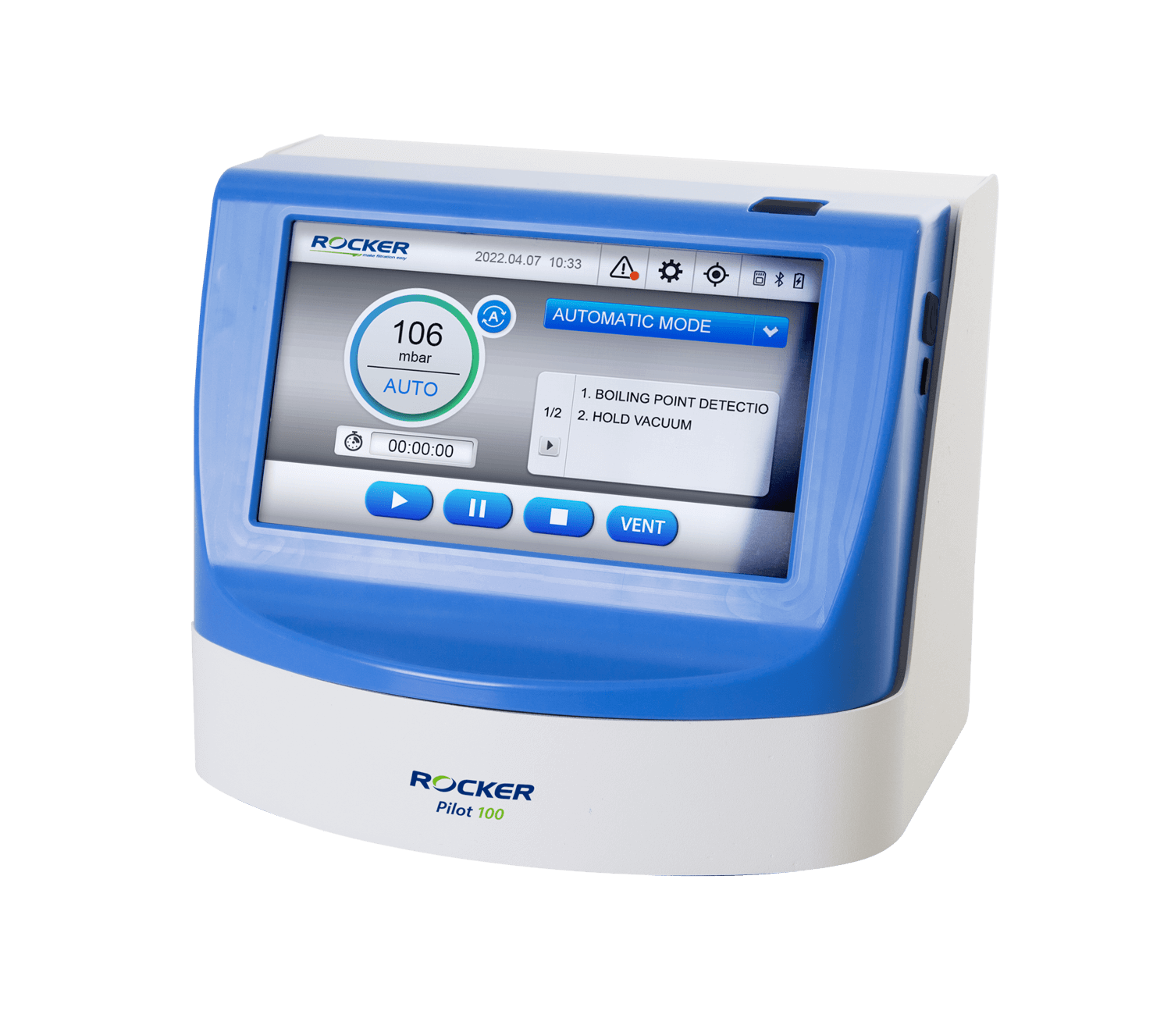
Both ROCKER’s vacuum controllers are equipped with auto boiling point detection. Feel free to start and leave.
– DC Chem 610 Pro Auto Vacuum System
– Pilot 100 Vacuum Controller
ROCKER’s Vacuum Controllers
Centrifugal concentrator for protein concentration
When it comes to the concentration of biological molecules such as proteins, DNA, RNA, another commonly used method is the concentration centrifuge tube, also known as ultrafiltration centrifuge tube, centrifugal filter, or purification column. This method requires the use of a centrifuge for operation. The principle involves ultrafiltration (UF), using a membrane to separate the target molecules.
Concentration centrifuge tubes are typically used in the purification, concentration, ultrafiltration, dialysis, desalting, solvent exchange, and other applications of small samples in the fields of biology and molecular biology. The operational process is relatively simple, usually involving placing the sample into the concentration centrifuge tube, using centrifugal force to pass the sample through the membrane, and separating and concentrating the target molecules based on the membrane pore size.
Additionally, because of the similar principles involved, concentration centrifuge tubes can also serve as preliminary tests for tangential flow filtration (TFF) systems. For more information on TFF, please refer to tangential flow filtration.
Centrifugal Vacuum Concentrator Applications
- Food safety testing, such as animal drugs, pesticide residues, additives, etc.
- Hospital laboratories, for the concentration of blood and urine metabolites, etc.
- Environmental analysis, including residual pesticides, environmental drugs, dioxins, hazardous environmental substances, etc.
- Biotech experiments, such as drying, purification, and concentration of proteins, DNA, RNA, etc.
- Ingredient extraction development, including traditional Chinese medicine, cosmetics, skincare products, food, dietary supplements, etc.
- Sample concentration and evaporation in fields such as clinical, biological, chemical, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, medical testing, etc.
References: